Understanding HVAC Essentials of Heating, Ventilation & AC
Understanding HVAC Essentials: Maintaining a comfortable indoor environment is crucial for homes and businesses alike. At the heart of this comfort is a system that controls the temperature, humidity, and air quality. Climate control is essential, and that’s where heating, ventilation, and air conditioning come into play.

A well-functioning system ensures that the air is fresh, clean, and at a comfortable temperature. This not only enhances the indoor environment but also improves the health and productivity of occupants. By grasping the HVAC basics, individuals can better appreciate the importance of proper system maintenance and operation.
What is HVAC? A Comprehensive Overview
At its core, HVAC encompasses the technologies used to control the temperature, humidity, and air quality in indoor environments. HVAC stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning, and it’s a crucial system for maintaining a comfortable and healthy indoor climate.
The Purpose and Importance of HVAC Systems
The primary purpose of HVAC systems is to provide a comfortable and healthy indoor environment. They achieve this by controlling the temperature, humidity, and air quality. This is important because it directly impacts the well-being and productivity of occupants. A well-designed HVAC system can improve indoor air quality, reduce the risk of health problems, and increase energy efficiency.
How HVAC Impacts Indoor Air Quality and Comfort
HVAC systems play a significant role in maintaining indoor air quality and comfort. They do this by circulating and filtering the air, controlling humidity levels, and maintaining a consistent temperature. Proper ventilation is also crucial, as it helps remove pollutants and stale air from the building. By controlling these factors, HVAC systems can significantly enhance the indoor environment, making it more comfortable and healthier for occupants.
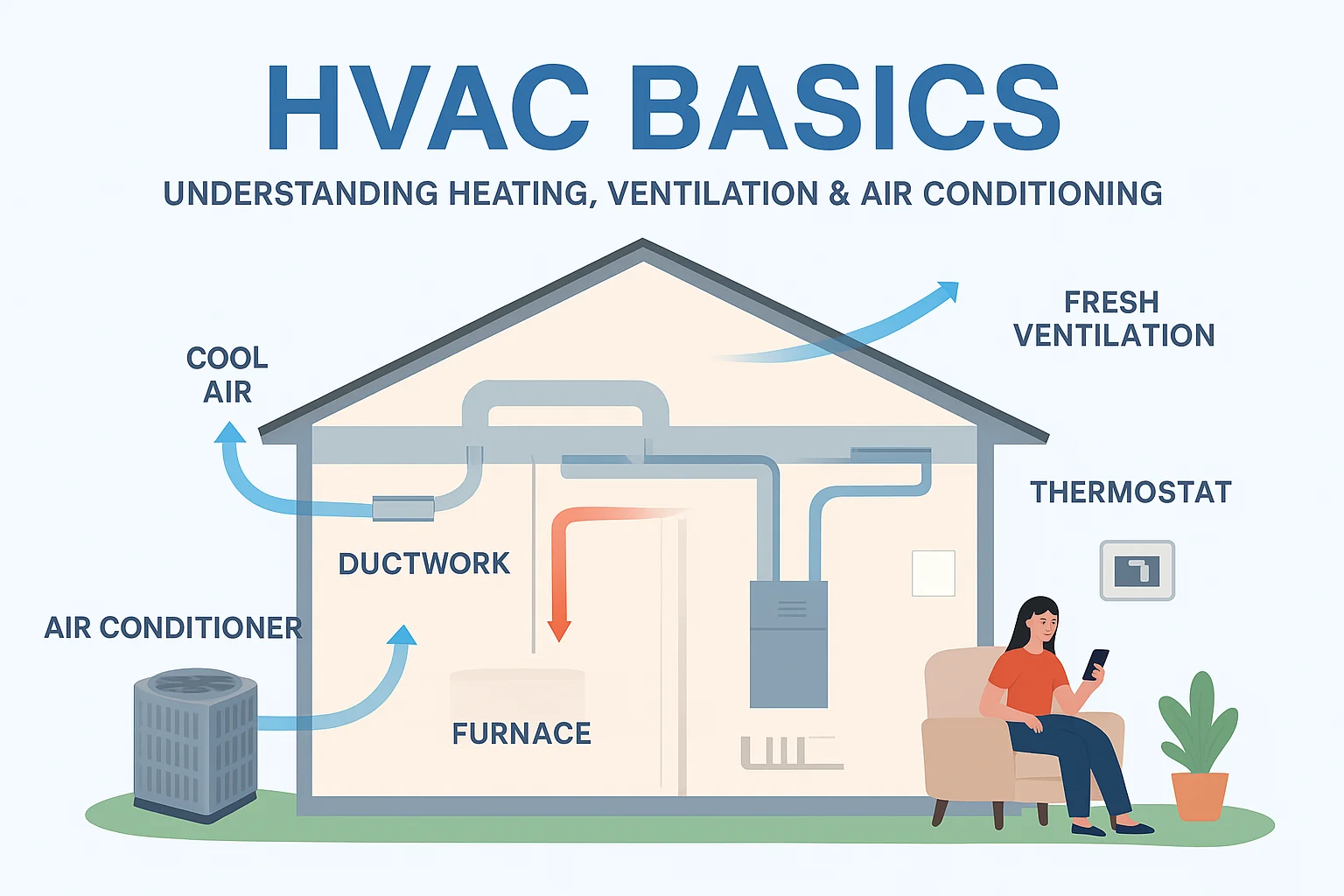
HVAC Basics: Understanding Heating, Ventilation & Air Conditioning
A well-functioning HVAC system is essential for maintaining a comfortable indoor environment. At its core, HVAC encompasses three primary functions that work in tandem to provide a seamless climate control experience.
The Three Core Functions Explained
The three core components of HVAC are heating, ventilation, and air conditioning. Heating systems, such as furnaces and heat pumps, warm the air. Ventilation systems ensure the circulation of fresh air, removing stale air and moisture. Air conditioning systems cool the air, controlling humidity levels.
How These Systems Work Together
These components don’t operate in isolation; they work together to maintain a consistent and comfortable indoor climate. For instance, during summer, the air conditioning system cools the air, while the ventilation system ensures that the air remains fresh. In winter, the heating system takes over, warming the air to a comfortable temperature.
Basic Terminology Every Homeowner Should Know
Understanding basic HVAC terminology can help homeowners communicate effectively with professionals. Key terms include “SEER rating” for air conditioners, “AFUE” for furnaces, and “thermostat.” Familiarity with these terms can aid in making informed decisions about HVAC maintenance and upgrades.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| SEER | Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio; measures air conditioner efficiency |
| AFUE | Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency; measures furnace efficiency |
| Thermostat | A device controlling the temperature of HVAC systems |
The Evolution of HVAC Technology
The HVAC industry has undergone significant transformations since its inception, driven by advances in technology and changing consumer needs. Over the years, the focus has shifted from basic heating and cooling to creating sophisticated systems that prioritize energy efficiency and indoor air quality.
Historical Development of Climate Control
The history of HVAC systems dates back to ancient civilizations, where simple methods were used to control indoor climates. The Romans, for instance, used hypocaust systems to heat their homes. The modern era saw significant advancements with the invention of mechanical refrigeration in the 19th century, revolutionizing air conditioning.
Modern Innovations in HVAC Systems
Today, HVAC technology continues to evolve with innovations like smart thermostats, inverter-driven compressors, and eco-friendly refrigerants. These advancements have significantly improved energy efficiency and reduced environmental impact.
| Innovation | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Thermostats | Learn temperature preferences and adjust accordingly | Energy Savings |
| Inverter-Driven Compressors | Adjust cooling capacity in real-time | Increased Efficiency |
| Eco-Friendly Refrigerants | Reduce environmental impact | Sustainability |
As HVAC technology continues to advance, we can expect even more efficient and environmentally friendly solutions to emerge, further enhancing indoor comfort and air quality.
Components of a Residential HVAC System
A residential HVAC system is made up of several key components that work together to provide a comfortable indoor environment. These components can be broadly categorized into primary equipment and secondary components, both of which are crucial for the system’s overall performance.
Primary Equipment: Furnaces, Air Conditioners, and Heat Pumps
The primary equipment in an HVAC system includes furnaces, air conditioners, and heat pumps. Furnaces are responsible for heating the home, typically using natural gas, propane, or electricity. Air conditioners cool the home by removing heat from the indoor air. Heat pumps can provide both heating and cooling by transferring heat between the indoors and outdoors.
Secondary Components: Thermostats, Ductwork, and Filters
Secondary components play a vital role in the efficient operation of an HVAC system. Thermostats regulate the temperature by controlling the HVAC system’s operation. Ductwork distributes heated or cooled air throughout the home. Filters clean the air by removing dust, pollen, and other contaminants, improving indoor air quality.
The Role of Refrigerants in HVAC Operation
Refrigerants are substances that change state from liquid to gas as they absorb heat from the indoor air, facilitating the cooling process. They are crucial for the operation of air conditioners and heat pumps. The choice of refrigerant can impact the system’s efficiency and environmental impact.
In summary, understanding the components of a residential HVAC system is essential for maintaining its efficiency and effectiveness. Regular maintenance of these components can help extend the system’s lifespan and improve indoor comfort.
Different Types of Heating Systems
Heating systems vary widely in terms of technology, efficiency, and application, catering to different needs and climates. Understanding these differences is crucial for homeowners to make informed decisions about their heating needs.
Forced Air Systems and Furnaces
Forced air systems, which include furnaces, are among the most common heating solutions. They work by circulating warm air through ductwork, providing quick and efficient heating. Furnaces can be powered by various energy sources, including natural gas, propane, and electricity.
Advantages: Fast heating, can be used with air conditioning systems, relatively affordable installation.
Considerations: Requires ductwork, can be noisy, filter maintenance is crucial.
Radiant Heating Options
Radiant heating involves installing heating elements (such as hydronic or electric systems) under the floor or within walls, providing warmth directly to objects and people. This method can be highly efficient and comfortable.
Benefits: Energy-efficient, quiet operation, can be used with various floor types.
Limitations: Higher upfront costs, installation can be complex, not suitable for all building types.
Geothermal and Heat Pump Solutions
Geothermal heating systems utilize the earth’s natural temperature to provide warmth, while heat pumps transfer heat from one location to another. Both are highly efficient and environmentally friendly.
Advantages: High efficiency, eco-friendly, can provide both heating and cooling.
Considerations: High initial investment, site-specific requirements, complex installation.
| Heating System | Efficiency | Cost | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forced Air Systems | Medium to High | Moderate | Moderate |
| Radiant Heating | High | Higher Upfront | Low |
| Geothermal/Heat Pumps | Very High | High Initial Investment | Very Low |
Each heating system has its unique characteristics, advantages, and limitations. By understanding these factors, homeowners can select the most appropriate system for their specific needs and circumstances.
Air Conditioning Systems Explained
The world of air conditioning encompasses a range of systems, each designed to meet specific cooling needs and preferences. Whether you’re looking to cool a single room or an entire home, understanding the different types of air conditioning systems available is crucial for making an informed decision.
Central Air Conditioning Functionality
Central air conditioning systems are a popular choice for whole-house cooling. They work by circulating cooled air through a network of ducts, providing a consistent temperature throughout the home. Central air conditioning is ideal for larger homes or for those who want a comprehensive cooling solution. These systems are typically more expensive to install but offer the advantage of being able to cool the entire house.

Ductless Mini-Split Systems for Zoned Comfort
Ductless mini-split systems offer a flexible alternative to traditional central air conditioning. They consist of an outdoor unit connected to one or more indoor units, which can be controlled independently to provide zoned comfort. This allows for more precise temperature control and can be more energy-efficient, as you’re only cooling the areas that need it.
Window, Portable, and PTAC Units
For those who don’t need whole-house cooling, there are several other options available. Window units are a simple and cost-effective solution for cooling single rooms. Portable units offer the flexibility of being moved from room to room, while PTAC (Packaged Terminal Air Conditioner) units are often used in hotels and can be installed through an exterior wall. Each of these options has its own set of benefits and is suited to different needs and situations.
Ventilation: The Often Overlooked Component
Ventilation, though often underemphasized, is a key element in ensuring that indoor air remains clean and healthy to breathe. It plays a crucial role in removing stale air and bringing in fresh air from outside, thus maintaining a healthy indoor environment.
Natural vs. Mechanical Ventilation Methods
There are two primary methods of ventilation: natural and mechanical. Natural ventilation relies on the natural airflow through openings such as windows, doors, and vents to exchange indoor and outdoor air. This method is cost-effective and energy-efficient but can be influenced by external factors like weather and outdoor air quality.
Mechanical ventilation, on the other hand, uses fans and ductwork to control the airflow, providing a more consistent and reliable means of ventilating a building. Mechanical systems can be designed to meet specific ventilation needs, making them suitable for a wide range of buildings and climates.
Energy Recovery Ventilators (ERVs) and Heat Recovery Ventilators (HRVs)
To enhance energy efficiency, Energy Recovery Ventilators (ERVs) and Heat Recovery Ventilators (HRVs) are used. ERVs transfer both heat and moisture between the incoming and outgoing air streams, while HRVs transfer heat only. These systems help in reducing the energy required to heat or cool the incoming fresh air, thus improving the overall energy efficiency of the HVAC system.
Addressing Indoor Air Quality Concerns
Proper ventilation is essential for maintaining good indoor air quality. By removing pollutants and excess moisture, ventilation helps prevent the growth of mold and reduces the concentration of indoor air pollutants. This is particularly important in modern, tightly sealed buildings where indoor air can become stagnant.
In conclusion, ventilation is a vital component of HVAC systems that should not be overlooked. By understanding the different ventilation methods and technologies available, homeowners and building managers can make informed decisions to improve indoor air quality and overall comfort.
Choosing the Right HVAC System for Your Home
The right HVAC system can make all the difference in your home’s comfort and energy bills, but selecting it requires careful consideration of various factors. When choosing an HVAC system, it’s essential to consider your home’s specific needs and the local climate to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
Climate Considerations and Regional Factors
Your local climate plays a significant role in determining the most suitable HVAC system for your home. For instance, homes in colder climates may require more robust heating systems, while those in warmer climates may prioritize air conditioning. Geothermal systems are an excellent option for many regions due to their high efficiency and ability to provide both heating and cooling.
Home Size, Layout, and Insulation Impact
The size and layout of your home, along with its insulation quality, significantly impact the type of HVAC system you should choose. A well-insulated home will require a less powerful HVAC system compared to a poorly insulated one. Proper sizing is crucial to ensure efficiency and comfort. Here are key factors to consider:
- Square footage of your home
- Number of windows and their orientation
- Insulation quality in walls, floors, and ceilings
- Layout and number of stories
Budget Planning: Initial Costs vs. Long-term Savings
While the initial cost of an HVAC system is a significant consideration, it’s equally important to think about long-term savings. Energy-efficient systems may have higher upfront costs but can lead to substantial savings on energy bills over time. Consider the following when planning your budget:
- Initial purchase and installation costs
- Operating costs, including energy consumption
- Maintenance and potential repair costs
- Potential rebates or incentives for energy-efficient systems
By carefully considering these factors, homeowners can make an informed decision when choosing an HVAC system that meets their needs, enhances their comfort, and saves them money in the long run.
HVAC Installation and Replacement Guidelines
When it comes to HVAC installation and replacement, there are several key guidelines to follow for optimal performance. A well-installed HVAC system ensures efficient heating and cooling, reduces energy consumption, and prolongs the system’s lifespan.
Proper Sizing and Load Calculations
One of the most critical aspects of HVAC installation is proper sizing. An incorrectly sized system can lead to inefficiencies, increased energy bills, and reduced comfort. Load calculations are essential to determine the correct size of the HVAC system for your home. This involves assessing factors such as the home’s size, insulation, window orientation, and local climate.
Professional Installation Best Practices
Professional installation is vital for the optimal performance of your HVAC system. Certified technicians ensure that the system is installed according to manufacturer specifications and local building codes. Best practices include verifying the system’s ductwork, ensuring proper refrigerant charging, and testing the system for optimal performance.
Permits, Codes, and Safety Requirements
HVAC installation and replacement must comply with local building codes and safety standards. Obtaining the necessary permits before starting the project is crucial. Compliance with codes ensures the system’s safety and efficiency. Additionally, following safety requirements protects both the installers and the homeowners from potential hazards.
| Installation Aspect | Importance | Best Practice |
|---|---|---|
| Proper Sizing | Ensures efficiency and comfort | Conduct thorough load calculations |
| Professional Installation | Guarantees optimal performance | Hire certified technicians |
| Permits and Codes | Ensures safety and compliance | Obtain necessary permits and follow local codes |

Maintenance Tips for Optimal HVAC Performance
Maintaining your HVAC system is vital for optimal performance, energy efficiency, and longevity. Regular maintenance not only ensures your system runs smoothly but also helps in identifying potential issues before they become major problems.
Seasonal Maintenance Checklist
To keep your HVAC system in top condition, it’s essential to perform seasonal checks. Before the heating season begins, inspect your furnace and heating components. Similarly, before the cooling season starts, check your air conditioning unit and associated parts.
- Inspect and clean filters
- Check thermostat settings and calibration
- Inspect ducts for leaks and damage
- Check electrical connections and components
Filter Replacement and Cleaning Procedures
Filters play a crucial role in maintaining indoor air quality and system efficiency. Regularly cleaning or replacing filters can significantly impact your system’s performance.
Tips for Filter Maintenance:
- Check filters monthly, especially during peak usage seasons
- Replace disposable filters according to the manufacturer’s schedule
- Clean reusable filters as recommended by the manufacturer
Professional Service Schedules and What to Expect
While DIY maintenance is helpful, professional service is indispensable for comprehensive system checks and complex repairs.
Benefits of Professional Service:
- Expert diagnosis of potential issues
- Comprehensive maintenance to prevent breakdowns
- Improved system efficiency and performance
Extending System Lifespan Through Proper Care
Proper maintenance is key to extending the lifespan of your HVAC system. By following a regular maintenance schedule and addressing issues promptly, you can significantly prolong the life of your system.
Actions to Extend System Lifespan:
- Regularly inspect and maintain system components
- Keep the area around the system clean and clear
- Ensure proper system sizing and installation
Smart HVAC Technologies and Future Trends
The integration of smart technologies in HVAC systems is enhancing energy efficiency and user comfort. This convergence of technology and traditional HVAC is revolutionizing the industry.
Smart Thermostats and Home Automation Integration
Smart thermostats are at the forefront of this revolution, offering users the ability to control their HVAC systems remotely through smartphones and voice assistants. This integration with home automation systems allows for seamless control and optimization of indoor environments.
Some key benefits of smart thermostats include:
- Enhanced energy efficiency through optimized temperature control
- Increased comfort with personalized temperature settings
- Remote monitoring and control capabilities
Energy Efficiency Innovations
Innovations in energy efficiency are a significant trend in the HVAC industry. New technologies and systems are being developed to minimize energy consumption while maintaining optimal indoor conditions.
Key innovations include:
- Advanced inverter technology for more efficient operation
- Smart sensors that detect occupancy and adjust settings accordingly
- Energy recovery ventilators that reuse energy from exhaust air
Sustainable and Eco-Friendly HVAC Solutions
The shift towards sustainability is driving the development of eco-friendly HVAC solutions. These include systems that use natural refrigerants, reduce waste, and are designed for recyclability.
As the HVAC industry continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative solutions that combine efficiency, comfort, and sustainability.
Conclusion: Making Informed HVAC Decisions
Understanding HVAC systems is crucial for making informed choices that impact your home’s comfort, energy efficiency, and overall climate control. By grasping the essentials of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, you can select the right system for your needs and ensure optimal performance.
Effective HVAC decisions involve considering factors such as climate, home size, and budget. With this knowledge, you can choose a system that provides the best balance between initial costs and long-term savings. Regular maintenance is also vital to extend the lifespan of your HVAC system and maintain its efficiency.
By applying the insights gained from this article, you can make informed HVAC decisions that enhance your home’s comfort and reduce energy consumption. Whether you’re installing a new system or maintaining an existing one, a well-informed approach will help you achieve optimal climate control and enjoy a more comfortable living space.
FAQ
What is the purpose of an HVAC system?
The primary purpose of an HVAC system is to maintain a comfortable indoor environment by controlling temperature, humidity, and air quality.
How often should I replace my HVAC filters?
It’s recommended to replace HVAC filters every 1-3 months, depending on usage, manufacturer recommendations, and personal preferences.
What are the benefits of a smart thermostat?
Smart thermostats offer benefits such as energy efficiency, remote temperature control, and personalized scheduling, which can lead to cost savings and enhanced comfort.
How do I choose the right size HVAC system for my home?
To choose the right size HVAC system, consider factors such as home size, insulation, climate, and load calculations, and consult with a professional for proper sizing.
What is the difference between a heat pump and a furnace?
A heat pump provides both heating and cooling by transferring heat, while a furnace generates heat through combustion or electric resistance, and is typically used for heating-only applications.
How can I improve indoor air quality with my HVAC system?
To improve indoor air quality, consider using a high-quality air filter, maintaining proper ventilation, and upgrading to a system with advanced air purification features.
What are the advantages of geothermal HVAC systems?
Geothermal HVAC systems offer advantages such as high energy efficiency, reduced energy costs, and environmental sustainability, by leveraging the natural temperature of the earth.
How often should I schedule professional HVAC maintenance?
It’s recommended to schedule professional HVAC maintenance at least once a year, ideally before the start of heating or cooling season, to ensure optimal performance and extend system lifespan.
Can I install a new HVAC system myself?
While it’s possible to install a new HVAC system yourself, it’s not recommended, as improper installation can lead to safety hazards, reduced efficiency, and costly repairs; it’s best to hire a licensed professional.
What are the benefits of ductless mini-split HVAC systems?
Ductless mini-split HVAC systems offer benefits such as zoned comfort, energy efficiency, and flexibility, making them ideal for homes without ductwork or with specific heating and cooling needs.
How do energy recovery ventilators (ERVs) work?
ERVs recover energy from exhaust air and transfer it to incoming fresh air, reducing the load on the HVAC system and improving indoor air quality, while conserving energy.


